If you've familiarized yourself with bitcoin, you've most likely experienced various price corrections. Every bull market has a pullback eventually.
Whenever there is a market downturn, one way to hedge the losses or even make a profit from a dropping price is by shorting.
In this guide, we'll go over the 6 different ways of shorting bitcoin, and other cryptocurrencies, while exploring some of the possible risks involved.
What is shorting?
Shorting is a financial strategy that allows traders to benefit from the downward trending prices of an asset. The objective of shorting is similar to general trading: buying low and selling high, but in reverse order.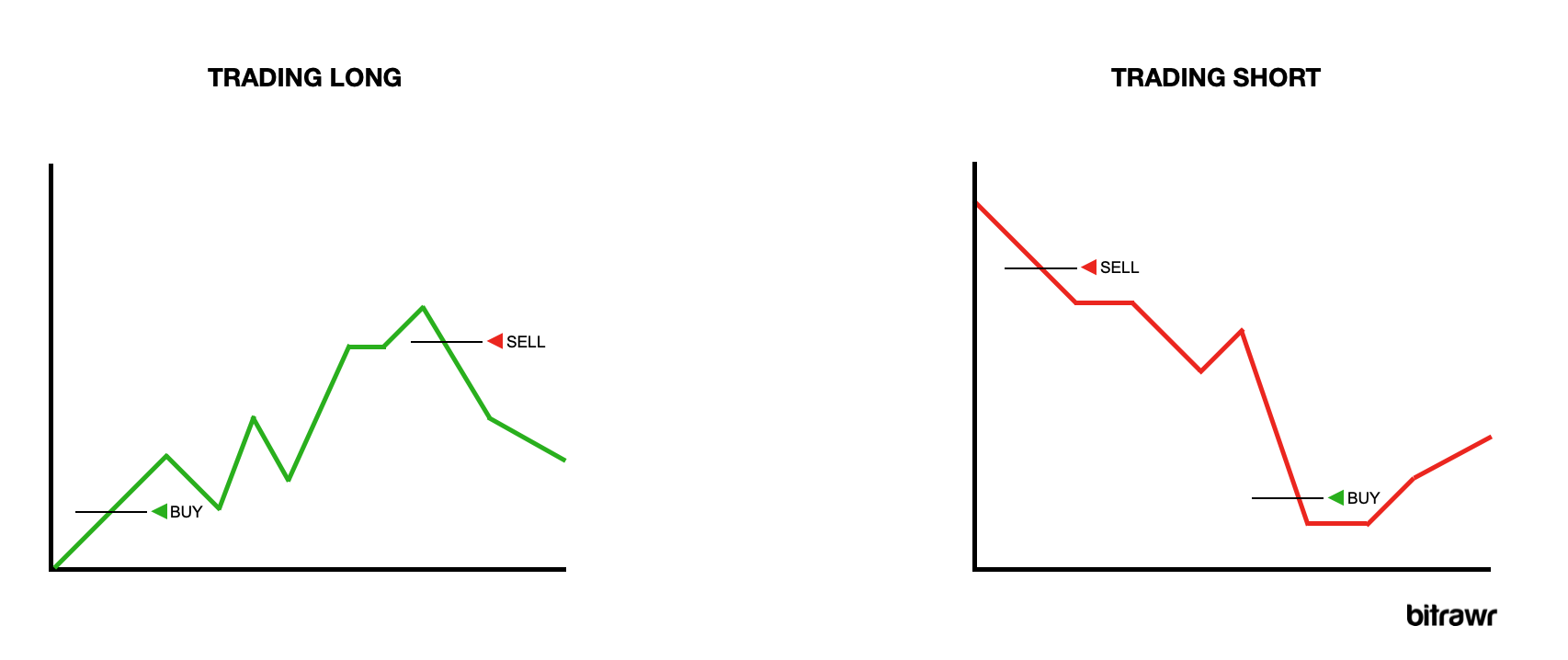
When a trader believes that the price of Bitcoin will go down, they will borrow Bitcoin and sell it now to buy back and repay their lender at a later stage, once the price has gone down.
To illustrate, let's assume you borrow and sell 10 BTC at $50,000 each. This means you've sold 10 BTC for $500,000. Once the price of bitcoin drops to $40,000, you buy back using the $500,000 (this time buying 12.5 BTC) and repay the borrowed debt of 10 BTC. After this trade, you have made a profit of 2.5 BTC or $100,000.
1. Margin Trading
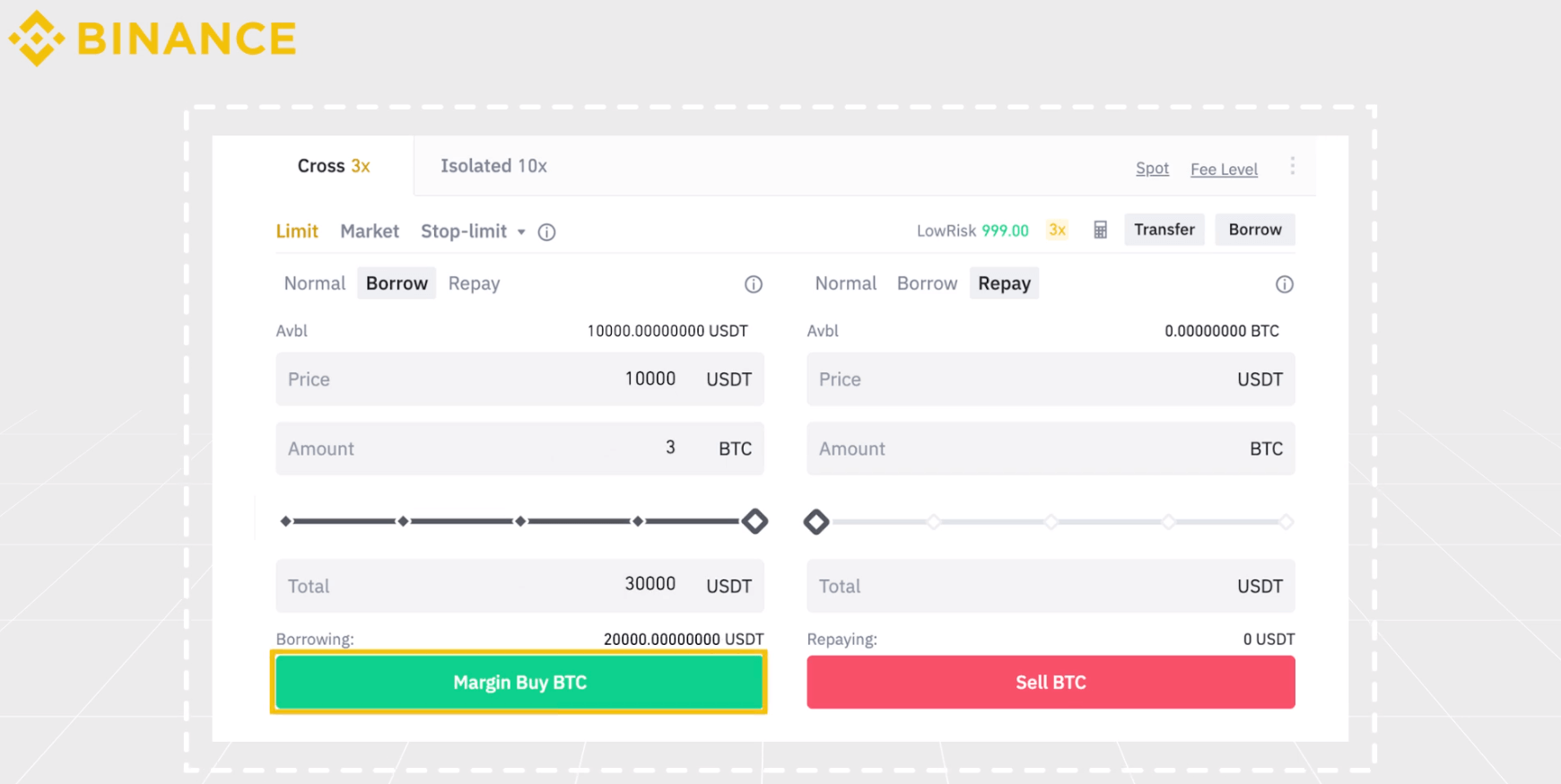
For anyone already registered and verified on some of the bigger cryptocurrency exchange platforms, margin trading will be one of the easiest ways to short bitcoin.
These are the best leverage trading Bitcoin and crypto platforms:
When trading on margin, traders actually borrow funds from the exchange and use that money towards leveraging their positions. Multiplying your exposure to the market allows small market movements to potentially turn into big profits (or losses).
With margin trading, you have the ability to trade in both directions, long or short and on some exchanges, like BitMEX or Deribit, you have the ability to speculate on price using up to 100x leverage.
However, depending on the jurisdiction you are in, margin trading might not be available to you.
If you're in such a location and still want to short bitcoin with a bit of leverage, you can try leveraged tokens.
These tokens mirror the price of an underlying asset, in this case bitcoin, and apply leverage.
So the 3x Short Bitcoin Token (BEAR) on FTX will increase 3x of whatever decrease bitcoin experiences. BTCUP and BTCDOWN on Binance will allow you to go long (or short) with BTC using up to 4x leverage.
The convenience when trading leveraged tokens is you can just buy and HODL them as you would any other crypto asset.
It's important to note that margin trading amplifies gains but can also lead to losses above the initially deployed capital. So any margin position has to be monitored closely.
2. Options
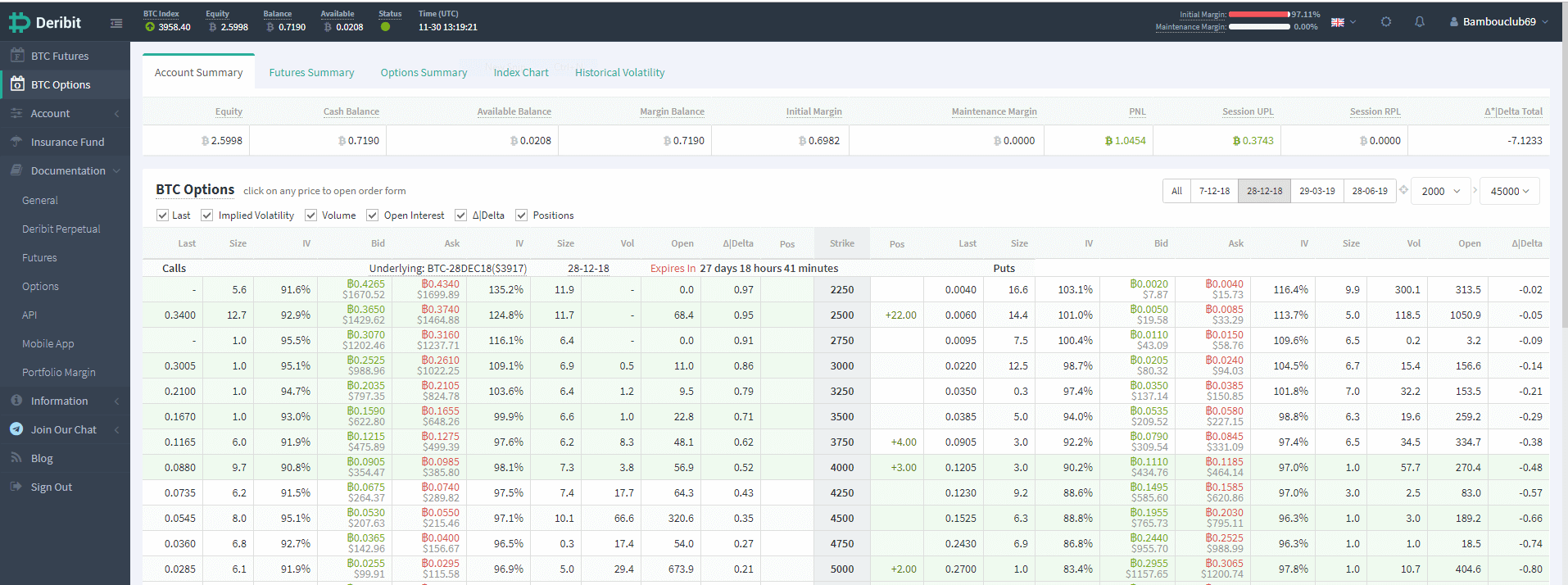
Options are a type of financial contract that is split into types: calls and puts. When buying an option, traders bet on the price of bitcoin at some later date.
Bitcoin call options - buying a call option means you are expecting that the price of bitcoin will increase in value over the period of the contract (usually 3 months). This allows you to buy an agreed-upon quantity of bitcoin at the strike price (the set price at which a contract can be bought or sold when it is exercised) when the option expires.
Bitcoin put options - buying a put option means you are expecting the price of bitcoin to go down over time. If the strike price at the end of the contract is higher than the current market price, you turn a profit.
Exchanges that offer Bitcoin options include Bakkt, Okex, LedgerX, FTX, and Deribit.
When picking a platform, consider the premium, which is a price paid by holders of the option calculated based on factors such as volatility, expiry, and spread between the current and the strike price (the price you can buy the asset at).
Overall, Options are complex financial instruments and not recommended for inexperienced traders. One benefit is that, when buying options, the maximum amount of money you can lose is the cost of the option premium.
3. Futures Trading
Trading futures is an easy way to speculate on the price direction of bitcoin at a specific time in the future.
When taking a long position, you agree to buy bitcoin at a specified price once the futures contract expires. You profit when the price of BTC is higher than the contract price.
Short positions are the inverse of this, profiting only when BTC is lower than the contract price.
Traditionally, futures contracts have particular dates at which trades have to be settled. However, in the world of crypto, one type of future runs without an expiry date - the so-called perpetual futures, or short perps for short.
With the volatility in crypto markets, it can be advantageous to trade a futures contract without an expiry date, where the counterparties hold their trade as long as they want to. The only costs you incur are the funding costs.
Most Bitcoin futures are tracking the price of Bitcoin relative to USDT (Tether-USD). Some exchanges will also allow you to leverage their perpetual futures, increasing potential profits and losses.
You can trade crypto futures on Kraken, FTX, Binance Futures, ByBit, and the decentralized exchange DYDX - among others.
4. CFDs
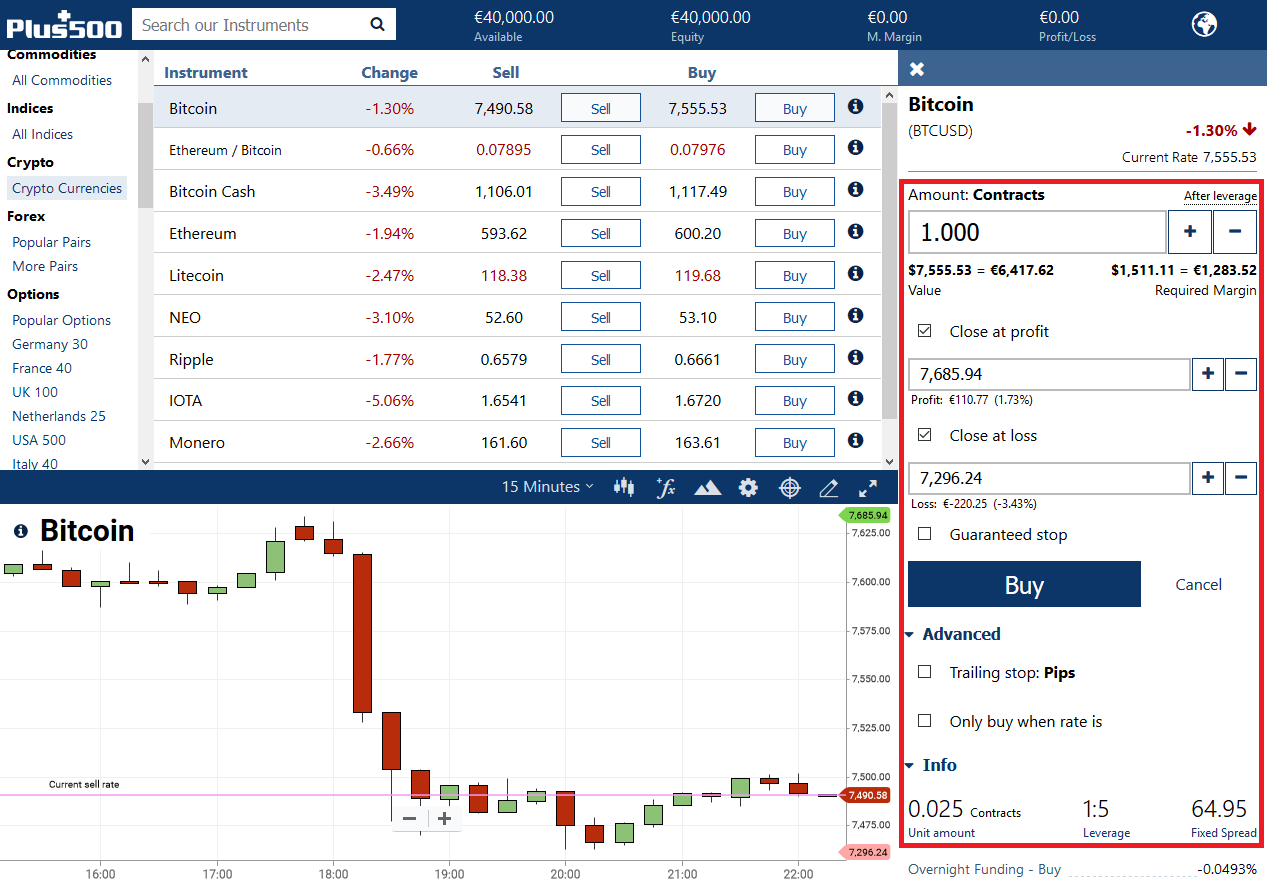
CFD is an acronym for contract for difference. Instead of borrowing bitcoin and repurchasing it to repay the lender, traders agree to pay the difference between the current and future price when entering a CFD contract. If the price of the asset declines, the broker will compensate traders for the difference resulting in a profit for the trader.
Unlike when trading on a crypto-exchange, there is no delivery of actual real bitcoin when trading CFDs, so you won't need a bitcoin wallet.
With Bitcoin CFDs, traders can use their traditional finance brokers to benefit from exposure to crypto-assets, without dealing with the technicalities that come with it. Consequently, there is no way to withdraw or deposit CFDs.
Bitcoin CFDs could be the right choice for traders that want to stay on their TradFi broker and not deal with the intricacies of cryptocurrency exchanges.
Reliable venues to trade Bitcoin CFDs include eToro, Plus500, OKEx, and AvaTrade. When picking a broker, check their fees, as some might charge overnight fees.
5. Inverse Exchange-Traded Products/ETF
Exchange-traded products & funds are financial instruments trading on exchanges, allowing investors to gain exposure to an underlying asset without ever purchasing the underlying.
As of today, there is one inverse exchange-traded ETP, the 21 Shares Bitcoin Short ETP, and one inverse ETF by Horizen. The first is trading in Europe, and the latter is available on the Toronto Stock Exchange.
Also, the first-ever Bitcoin Futures ETF in the US started trading at the NYSE in October of 2021. The ProShares Bitcoin Strategy ETF goes by the ticker name of BITO and saw around $1 billion of trading volume on the first day.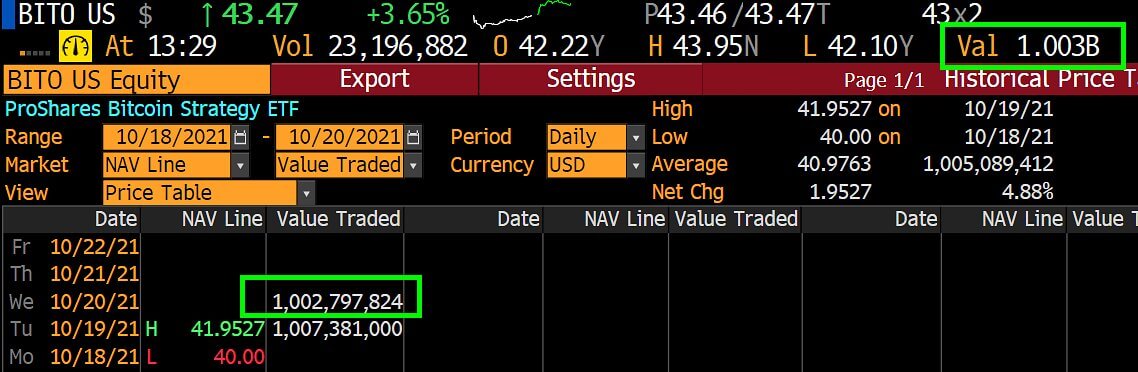
Whenever Bitcoin's price decreases, both products increase in price, offering investors an easy way to speculate on a price drop.
The benefits of these regulated offerings include, that they provide institutional-grade security and collateralization by the broker, making them especially attractive for institutions.
6. Prediction Market
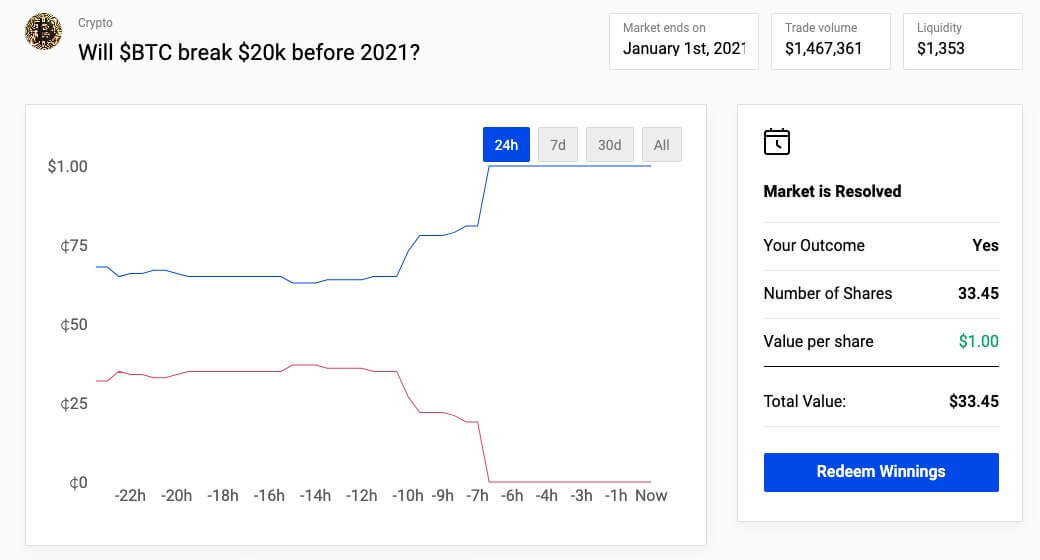
While not exactly a way to short bitcoin, prediction markets still provide a feasible way to benefit from a price drop of the digital gold.
Prediction markets are derivatives basing their value on the probability of a certain event occurring. In this case, it's determining what the price of bitcoin will be on a certain fixed date.
You just need to create an event if one doesn't already exist on a prediction market like Polymarket. As long as someone else takes up your bet and your prediction comes true, you will receive money from them.
Benefits of shorting
When done correctly, shorting can provide various benefits:
- Hedge portfolio risk: if you believe Bitcoin to be overvalued, shorting is a great way to benefit from it in the short term. Even if Bitcoin goes down, your short will offset the loss in value.
- Profit in a bear market: markets come in cycles; crypto isn't different in that regard. When shorting Bitcoin, you can benefit even during market downturns.
- Volatility: by shorting Bitcoin during dips, you can make the most of the market volatility. This can be done even on short time-frames with significant profit when leverage is applied.
While shorting has attractive benefits, it's worth noting that it's still a significantly higher risk than just buying and selling bitcoin.
Additionally, it requires exact timing and constant monitoring. As hedge funds can testify, the last position you want to find yourself in is trying to desperately cover your short during a short squeeze. Shorting is best applied as part of a broader trading strategy.
Conclusion
Overall, if and how you can short bitcoin might not only depend on your personal preferences for traditional broker vs. crypto exchanges but also your jurisdiction.
When looking to short, you might want to take a few hints from events that in the past have triggered the market to drop, such as hostile regulatory action, failure of major exchanges, and the hard fork risk back during the SegWit wars.
Before shorting bitcoin, ensure you understand the type of order you're using and ensure that you have a plan on when (if applicable) you cut losses and exit your short position.
Shorting isn't for the faint-hearted. That being said, if you take well-calculated risks, and use shorting to hedge against others, it can pay off quite handsomely.

