In the early days, long before Bitcoin’s creation, there were only cypherpunks.
Cypherpunks were a movement of individuals, starting in the 1980s, who were fascinated by the advancement of information technology and strong encryption.
These individuals set goals to provide liberatory technologies for people, accessible to anyone on the planet, who have access to a computer.
Cypherpunk history - Wired Magazine issue #2 May 1993, Crypto Rebels.
Ever since governments started controlling and employing surveillance over the internet, it has become an important task for the cypherpunks to allow anyone to bypass these restrictions or sanctions in order to be able to freely communicate.
But it wasn't just individuals from authoritarian countries, the technology was benefiting everyone.
With strong encryption, their goal was to establish a free domain where everyone was able to connect with anyone, without limitations set by governments on these interactions all based on a voluntary ethos.
This ideology of freedom was so strong on the internet that John Perry Barlow in 1996, set out his vision in his manifesto called “A Declaration of the Independence of Cyberspace”. He proclaimed the core tenets of these freedoms should also apply to the internet.
Since everything began gaining strength with the advent of strong encryption, like email, chat messaging or voice communication (VoIP), it was just a matter of time before the creation of an internet protocol money that lives right on the internet, in a distributed way.
The concept of peer-to-peer money at that time was still a dream for many cypherpunks. As new technologies started coming together, the future building blocks of Bitcoin were being created for Satoshi to later be able to puzzle it all together.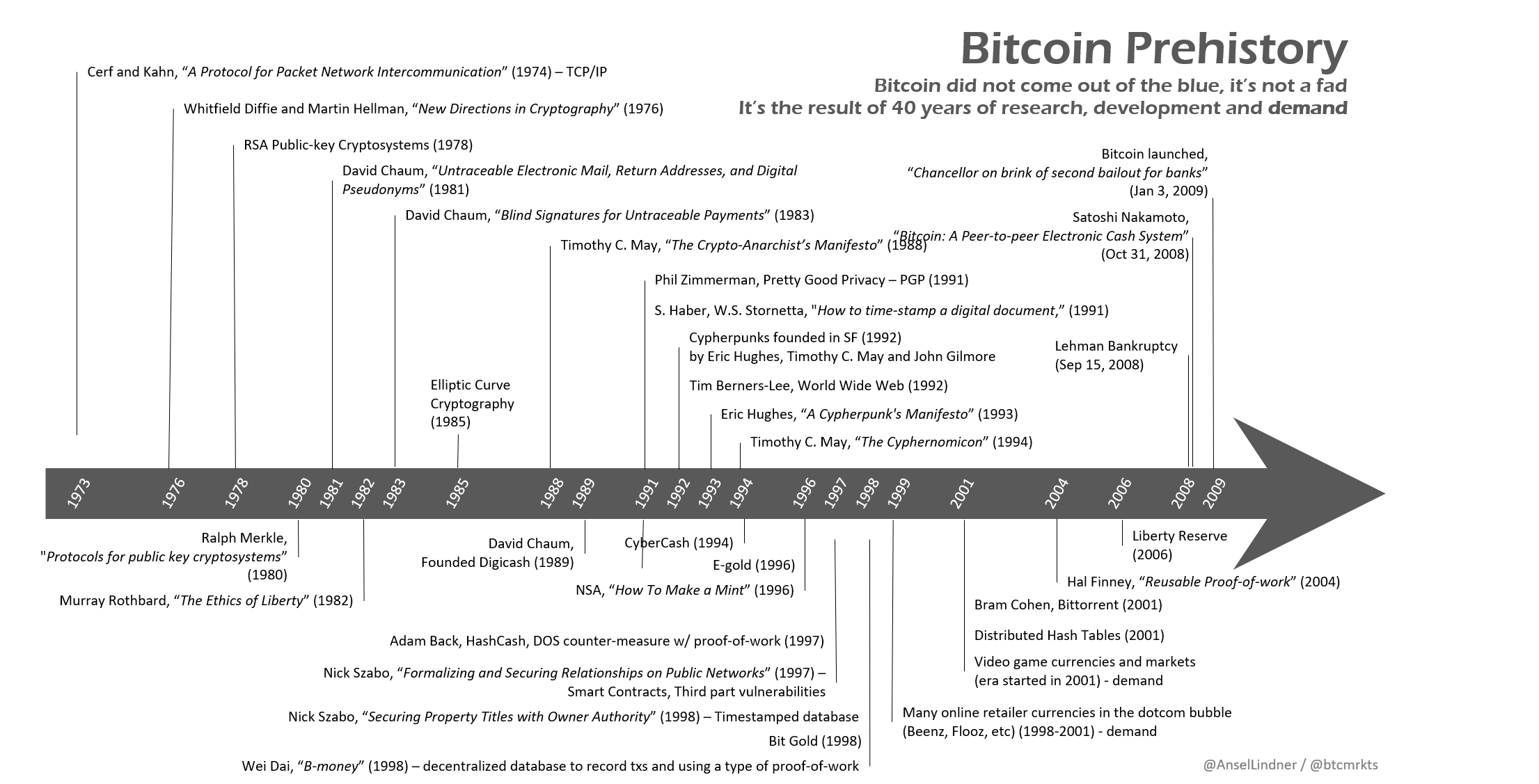
It's due to the contributions of people like David Chaum, Adam Back and others (also inventions like the NSA's one-way hashing algorithm SHA2) that Satoshi was able to put all the pieces together to be able to create Bitcoin.
Let’s take a deeper dive into the world of cypherpunks before the Bitcoin political world.
The Cypherpunk Connection
Mathematics is the foundation of all cryptography. Even before computers, the mathematics branch of cryptography worked on creating encryptions, so-called ciphers, to create encoded communication.
Most notably, during World War II, Nazi Germany was using the Enigma machine to communicate secretly scrambled messages without the Allies discovering their plans.
Without knowledge of the ever-changing codebook to decipher the messages sent on Enigma, spying on German communications during the war became difficult, giving them the initial upper hand in the war.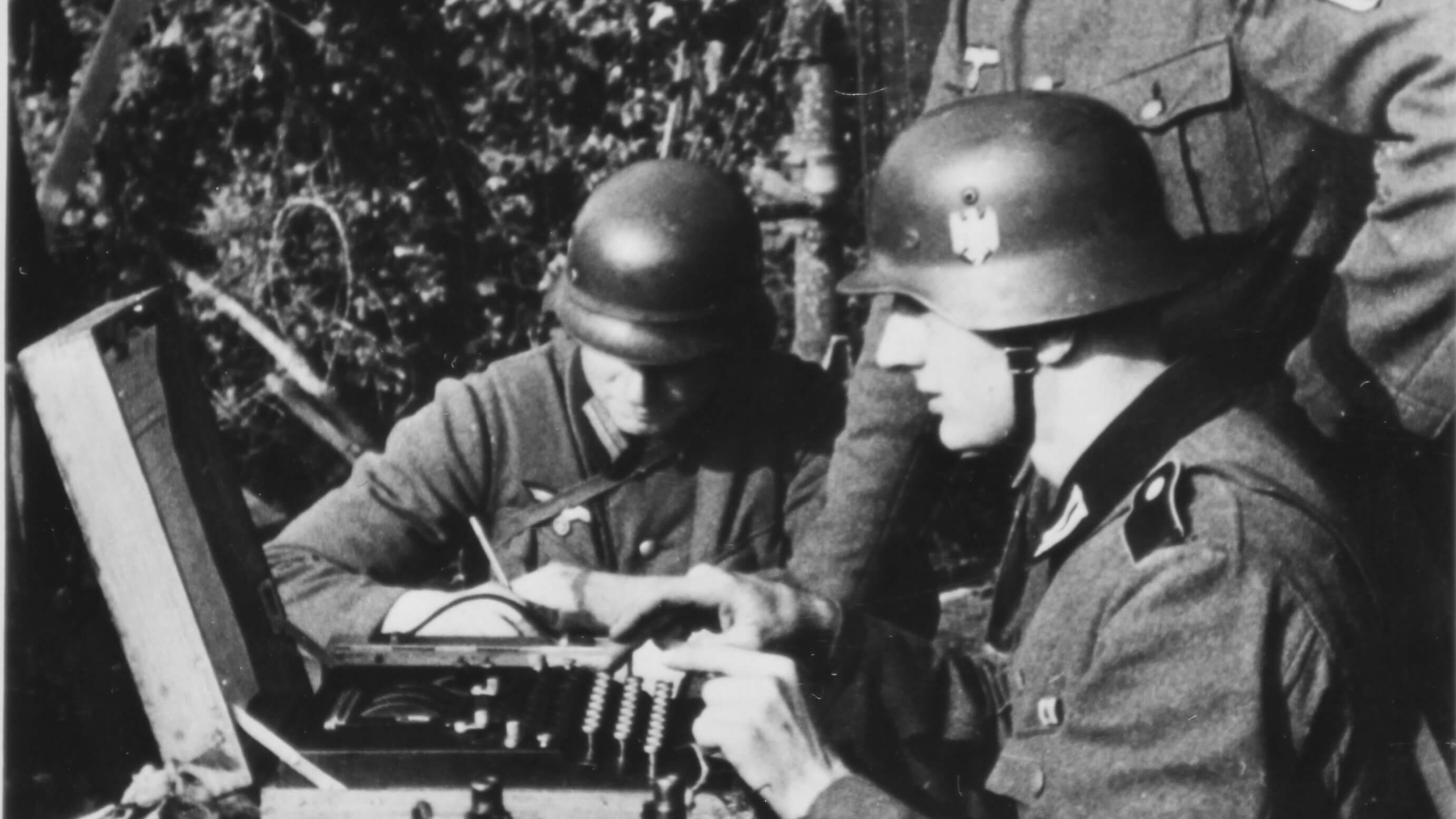
June 27, 1940 - Germans set up their most sophisticated coding machine, Enigma, to transmit information in their newly occupied French territory.
Allied cryptologists, most notably Alan Turing, were eventually able to exploit weaknesses in the Enigma machine with many historians believing that this helped accelerate the end of World War II by years.
It was cryptography that Turing had so admirably wrestled with in the 1940s, but it's also without cryptography that the world could easily be a devastating surveillance dystopia.
As computers and the internet were catching on in the 1990s, cryptography was thought of as a way to liberate individuals and break down the overreaching power of government. Since freedom on the internet was so substantial, it only needed the right tools to make it almost permanent in effect.
Phil Zimmerman, the creator of PGP encryption software, greatly contributed to the fight for privacy. His work helped kick off the race to create easily accessible encryption standards and methods that anyone can easily access to circumvent government surveillance.
At that time, the governments were so afraid of publicly accessible encryption they began attacking every attempt to create them and distribute them. They went as far as to ban the export of cryptography to foreign countries and arrest mathematicians who worked on new cryptographic standards
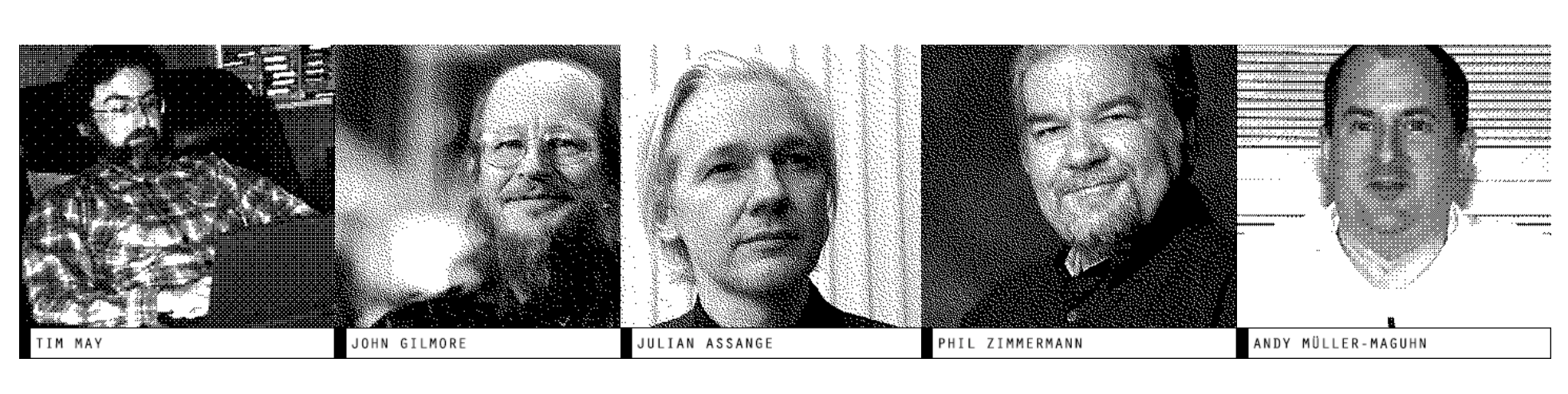

Notable Cypherpunks - The Verge.
This marked beginning of the fight for privacy and freedom. The US Government and their attempts to shut down cypherpunks were in direct violation of the First Amendment since mathematics and code is simply Free Speech.
During the Crypto Wars in the 90s, inventive methods were made to challenge government overreach and force the US Government to back down. The publishing of PGP’s whitepaper as a book for universities around Europe directly challenged the International Traffic in Arms Regulations, and along with many other attempts the US Government backed down and cypherpunks won the Crypto Wars in 1997.
This was an immense win for humanity because it allowed other inventions like SSL to be used broadly, as a common standard on the web to encrypt sensitive communication.
Without the existence of these technologies, it's the belief of many, that we would be in an interconnected world that more resembles the world within George Orwell’s book, 1984.
The Libertarian Connection
A Libertarian is a person who advocates for civil liberty and believes in the doctrine of free will.
This might be a not-so-alien concept for many because most might consider ourselves to be free human beings without anyone controlling our actions and personal choices, but it is far from that.
The Hayekian ideology of freedom and free commerce was a major basis of ideology for cypherpunks. Friedrich Hayek was an economist who popularized the idea of Austrian Economics, a world view that runs on the properties of free markets and sound money that cannot be inflated by a single nation-state.
Austrian Economics, at its' core, is a freedom-oriented economic theory where all human connections and transactions are voluntary and are free from coercive government authority and threats of violence from the State. Under this theory, where no government interference in the economy and money exists, free markets are able to flourish, and participants enjoy prosperity.
If human economic actions were left to operate in a natural state, Austrian economic theory would better describe the way the world would operate in. It is also how the world operated for millennia when gold was used as currency.
But this is not the case anymore. Since 1913's Federal Reserve Act, the world has changed to the standard of Central Banking.
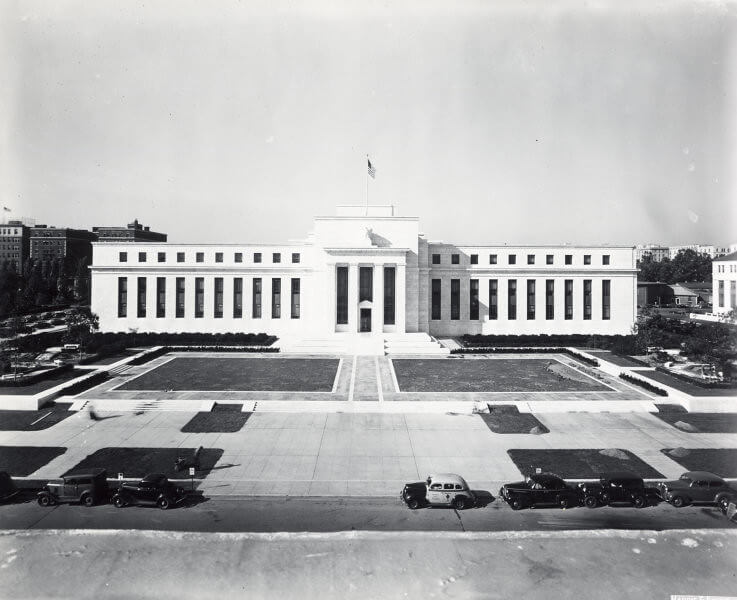

The 1913 Federal Reserve Act introduced a central bank to oversee monetary policy in the United States. The Eccles Building is the main office of the Fed in Washington D.C.
Since money is the main monopoly of the State, it wields great power over society. Today’s world is operating on the Keynesian Economic Theory, where the State (the one entity that controls the issuance of the money) can freely inflate the supply of money with the use of a Central Bank.
In this economic theory, the focus on spending emphasizes that individuals should not save in the long term, because we can accelerate our spending, in order to raise the GDP, and create more prosperity with it in the short term.
Austrian vs. Keynesian on the business cycle theory
But this could be nothing but far from the truth that Keynes concocted. The application of his economic theory resulted in rampant inflation and the destruction of capital. Since the State enforces the use of a given national currency on its territory (through the threat of violence) it has ultimate free reign to do whatever it wants with its own money supply.
As someone produces money and creates savings, the State collects taxation and proceeds to inflate the money supply, essentially stealing value away from those who earn its currency.
The effects of Monetary Nationalism (monetary socialism, or institutionalized system of time theft) is extremely destructive. Inflation in effect changes the behaviour of society and has the ability to entirely collapse it.
When savings are wiped out, society reaches for credit to be able to consume the necessary or unnecessary goods governed by its time preference.
When time preference is raised, everyone wants everything as fast as possible because when your money is rapidly losing value and the loan you picked up is also losing value, you have to spend it as fast as possible as you can. This leads to you spending your money way ahead into the future and putting yourself into total debt, without the possibility to afford savings.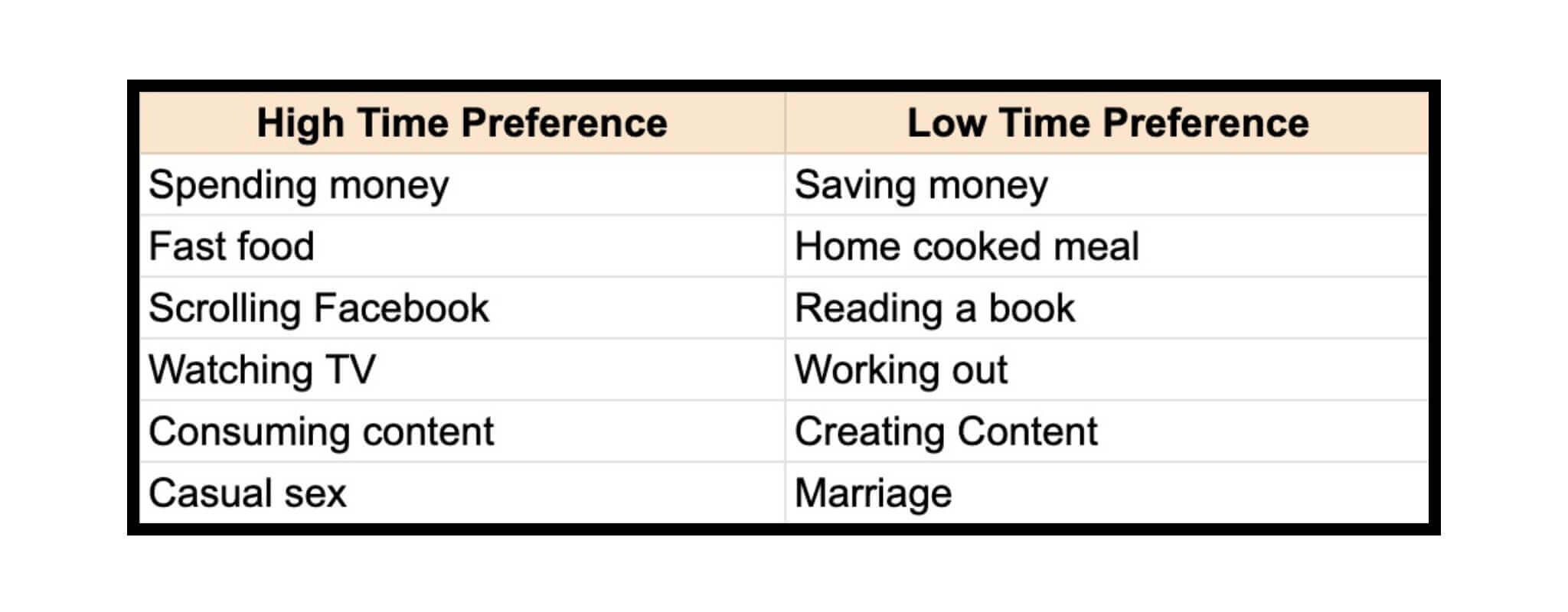
High time preference thinking is more concerned with the needs of the present moment, whereas low time preference thinking delays present gratification and places more emphasis on future needs - Image Source
The removal of the gold standard in 1971 by US President Richard Nixon was the ultimate end game of the US government's power to put the world entirely on a "Fiat Standard". This decision not only affected the US population but had ripple effects across the entire world.
Venezuela, Argentina, Turkey and Lebanon are fine displays of these destructive effects and processes that can put everyone into permanent poverty.
Libertarians are a vocal critic of this system because they understand the level of violence the State holds over everyone with one centralized currency (that nobody else other than the government is allowed to print out more of). This has led them to seek currencies that the state can not control or manipulate.
Gold and silver were always sought out throughout history since they were considered great stores of value. But since the State managed to gain ultimate access to these monetary metals, it was also able to control its production and price.
The US Government does not shy away from confiscating its citizens' property. Proclamations like Executive Order 6102 confiscated the private gold holdings of citizens in 1933. Violation of the order was punishable by fines of up to $10,000 or up to ten years in prison, or both.
This is why in recent years gold has become considered a less safe store of value considering it can be easily confiscated, it is very hard to transport, and its storage is often very expensive.
At this point, you can see why someone would have wished for something better, something like a store of value not controlled by one entity, but nothing of the sort existed.
In the 2000s the Cypherpunk movement slowly started to disappear. It was only until the events of the 2008 Financial Crisis and the sudden appearance of Satoshi Nakamoto with his creation of Bitcoin, that everything began to change.
The Bitcoin Connection
The creation of Bitcoin was a direct message to the central bankers and banking institutions.
The Genesis Block (the first entry of Bitcoin's financial ledger) of Bitcoin embeds the headline from the front page of The Times newspaper, “The Times 03/Jan/2009 Chancellor on brink of second bailout for banks”.
It is now embedded in history forever as a testament to the fight against the evils of central banking.
The Libertarian and Austrian Economics’ theory has long thought of ways it could separate money from State, liberate individuals, and make global commerce more free and prosperous, but there was no answer to it until Bitcoin came along.
What Bitcoin achieved is revolutionary. The network is not manipulated by state entities and it runs on the free market where individuals voluntarily interact with each other.
Bitcoin eliminates the State’s control over currency and allows everyone to do whatever they want with their money in a way they want to. Since almost everyone now has access to the internet, Bitcoin filled the gap that allows everyone to have access to a monetary network they can use to transact with anyone, without a government or a third party blocking their attempts.
On a much freer economic footing, we no longer have to rely on exchange rates and it gets a lot easier to transact with one global currency that everyone accepts.
By removing the State’s power, we can also restore confidence in savings, because our savings will no longer evaporate in value. This is due to the fact that there can be no more than 21 million bitcoins ever created since it is mathematically fixed in its code.
By restoring savings, sound economic principles begin to return, and the negative effects of inflationary currency can begin to slowly subside.
As more people have access to savings, their confidence in capital building will accelerate their ability to build generational wealth and to commit to creating families, and create enterprise through entrepreneurship.
The World of Sound Money During Hyperbitcoinization
In a world of sound money, we no longer spend our money on useless junk. Our consuming behavior changes to a more sustainable format where our savings and preference for better goods dictate our purchasing actions.
As we are no longer affected by high time preference, we build greater generational wealth and legacies for larger families that one can create.
A "hyperbitcoinized" world would be much more free and open, but not necessarily less dangerous since the individual responsibility for one’s self becomes a major driver behind human action.
Unsustainable investments and government spending would be a thing of the past, and governments would be competing for our participation by providing the best of all services money can buy. This way makes governments profitable and more focused on the improvement of living standards, assurances to freedom, and upholding of acceptable just laws.
Bitcoin as of today is actively liberating individuals around the world. In places like Nigeria, a recent survey showed that about 32% of responding individuals use or interact somehow with Bitcoin.
As El Salvador slowly leads the adoption of Bitcoin, we can only guess what will be the future implications of Bitcoin to the world and the world economy to come.


